Dog Periodontal Disease Stages is a sneaky, yet common, issue that can cause serious problems if left unchecked. It’s crucial for dog owners to understand the various stages of periodontal disease to keep their furry friends healthy and happy. Let’s find out in this Dogs Infor article!
What is Periodontal Disease?
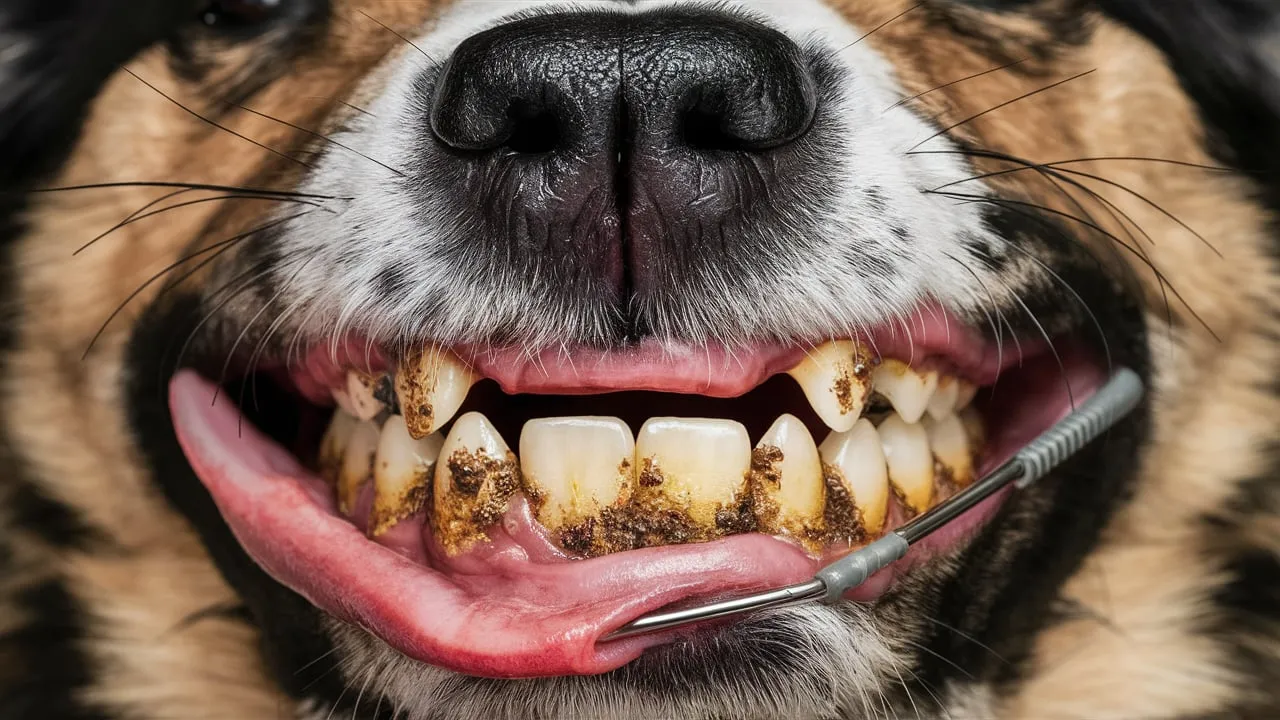
Periodontal disease is a common condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It’s caused by a buildup of plaque and tartar, which irritate the gums and create an environment where bacteria can thrive.
The Basics of Dog Dental Health
Just like humans, dogs need good dental hygiene to maintain their overall health. Here’s a breakdown of the basics:
- Plaque: A sticky film that forms on teeth. It’s made up of bacteria, food particles, and saliva.
- Tartar: Hardened plaque that can’t be removed by brushing alone. It irritates the gums and can lead to periodontal disease.
- Gingivitis: Inflammation of the gums, the first stage of periodontal disease.
- Periodontal Pockets: Spaces that form between the teeth and gums as the gums recede. These pockets can trap bacteria and make it difficult to clean.
- Bone Loss: As periodontal disease progresses, it can damage the bone that supports the teeth. This can lead to loose teeth and eventually tooth loss.
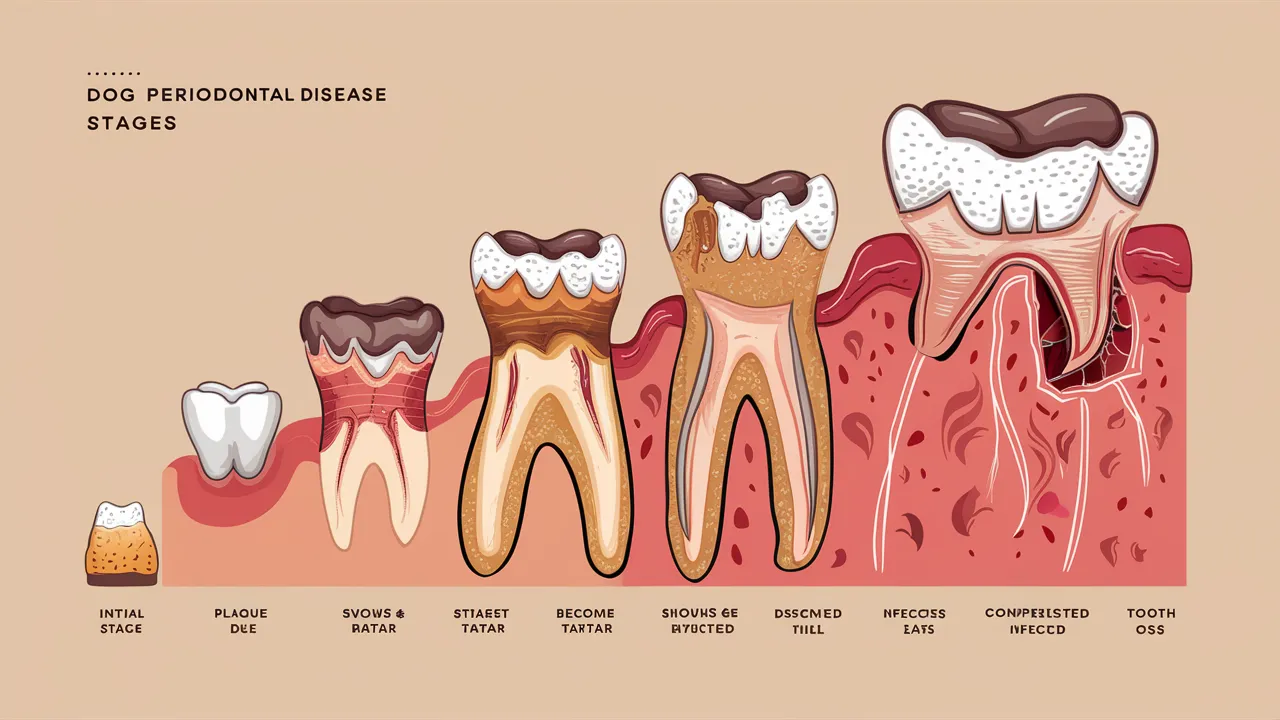
The Stages of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease progresses through several stages:
Stage 1: Gingivitis
- Gums are red, swollen, and may bleed easily.
- There is no bone loss.
- This stage is reversible with proper dental hygiene.
Stage 2: Early Periodontitis
- Gums are receding, creating pockets between the teeth and gums.
- Some bone loss occurs.
- This stage is still reversible with treatment, but it’s more difficult to treat than gingivitis.
Stage 3: Moderate Periodontitis
- Gums are significantly receding, and pockets are deeper.
- Bone loss is more extensive.
- Teeth may become loose.
- This stage requires more extensive treatment, such as scaling and root planing.
Stage 4: Advanced Periodontitis
- Gums are severely receding, and pockets are very deep.
- Extensive bone loss has occurred.
- Teeth are loose and may be lost.
- This stage may require tooth extraction.
It’s important to note that periodontal disease can be painful for dogs and can lead to other health problems, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and liver disease. Regular dental care, including brushing, professional cleanings, and dental diets, can help prevent periodontal disease.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Recognizing the signs of periodontal disease early on is crucial for preventing further damage and ensuring your dog’s comfort.
Early Signs
- Bad breath: A common sign of plaque and tartar buildup.
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums: Indicates inflammation and gingivitis.
- Receding gums: The gum line appears to be pulling away from the teeth.
- Yellow or brown tartar buildup: Visible on the teeth.
- Increased drooling: May indicate discomfort or pain.
- Loss of appetite: A sign that chewing is painful.
- Sensitivity to touch: Your dog may flinch or react when you touch their mouth.
Advanced Signs
- Loose teeth: A sign of significant bone loss.
- Pus discharge: May be present around the teeth or gums.
- Painful chewing: Your dog may avoid eating hard food.
- Weight loss: Due to difficulty eating or pain.
- Facial swelling: Indicates infection or abscess formation.
- Tooth loss: The most severe sign of advanced periodontal disease.
Preventive Measures for Periodontal Disease
Daily Dental Care Routines
Just like us, our furry friends need a good dental hygiene routine! Brushing their teeth daily is the best way to remove plaque and tartar buildup, which are the main culprits behind periodontal disease.
- Start Early: Get your pup used to brushing their teeth from a young age. Start with a finger brush and a pet-safe toothpaste, and gradually introduce a toothbrush as they get comfortable.
- Make it Fun: Turn brushing into a positive experience! Use treats, praise, and gentle encouragement.
- Be Patient: It might take some time for your dog to get used to brushing. Don’t give up!
Use of Dental Chews and Toys
Dental chews and toys offer a fun way to maintain clean teeth. They help remove plaque and tartar while freshening breath.
- Select the Right Chews: Choose chews designed for dental health, made with safe ingredients.
- Supervise Chewing: Always watch your dog while they chew, as some toys can break into small pieces that pose a choking risk.
Importance of Regular Veterinary Check-Ups
Just like we visit the dentist, our furry friends need regular dental check-ups too! Veterinarians can examine your dog’s teeth and gums, clean their teeth professionally, and catch any early signs of periodontal disease.
- Yearly Checkups: Schedule a dental checkup for your dog at least once a year.
- Early Detection is Key: Catching periodontal disease early can make treatment easier and more effective.
Conclusion
Periodontal disease poses a significant threat to your dog’s overall health. Understanding its stages and implementing preventive measures can help maintain your dog’s dental health. Be sure to brush their teeth regularly, offer dental chews, and arrange for professional cleanings. Early detection and treatment are crucial for avoiding serious dental issues.

Related Post
Signs Your Dog Needs Probiotics: Digestive Problems
Green Stool In Dogs: Causes, Concerns And When To Worry
Dental Anatomy Of Dogs: Unveiling The Secrets